Short-term, or current liabilities, are liabilities that are due within one year or less. They can include payroll expenses, rent, and accounts payable (AP), money owed by a company to its customers. Liabilities consist of many items ranging from monthly lease payments, to utility bills, bonds issued to investors and corporate credit card debt. Accounts payable represents money owed to vendors, utilities, and suppliers of goods or services that have been purchased on credit. Most accounts payable items need to be paid within 30 days, although in some cases it may be as little as 10 days, depending on the accounting terms offered by the vendor or supplier. These include the ownership of tangible assets, financial resources, and accounts receivable and inventory.
How to Create a Financial Forecast
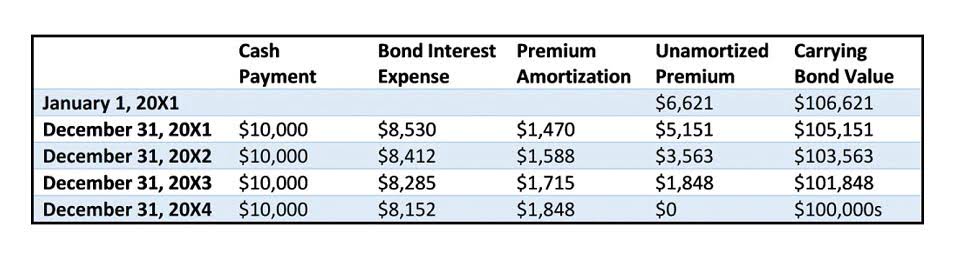
- Companies of all sizes finance part of their ongoing long-term operations by issuing bonds that are essentially loans from each party that purchases the bonds.
- The Ascent, a Motley Fool service, does not cover all offers on the market.
- As a small business owner, you’re going to incur different types of liabilities as you operate.
- A contingent liability is an obligation that might have to be paid in the future but there are still unresolved matters that make it only a possibility, not a certainty.
- Most often the portion of the long-term liability that will become due in the next year is listed as a current liability because it will have to be paid back in the next 12 months.
- A similar ratio called debt-to-assets compares total liabilities to total assets to show how assets are financed.
Other line items like accounts payable (AP) and various future liabilities like payroll taxes will be higher current debt obligations for smaller companies. Liabilities are listed on a company’s balance sheet and expenses are listed on a company’s income statement. Expenses can be paid immediately with cash or the payment could be delayed which would create a liability. Long-term liabilities are financial obligations of a company that extends more than a year. These liabilities affect a company’s financial structure because they indicate the amount of debts you have acquired to finance your assets and business operations.

What is a Liability Account? – Definition
Most state laws also allow creditors the ability to force debtors to sell assets in order to raise enough cash to pay off their debts. When a company determines that it received an economic benefit that must be paid within a year, it must immediately record a credit entry for a current liability. Depending on the nature of the received benefit, the company’s accountants classify it as either an asset or expense, which will receive the debit entry. For instance, assume a retailer collects sales tax for every sale it makes during the month. The sales tax collected does not have to be remitted to the state until the 15th of the following month when the sales tax returns are due.
The debt ratio
If the liabilities are more, the working capital of the company is reduced. A normal operating cycle is the time frame needed to convert money to raw materials, finished products, sales, accounts receivable, and money back again. This decision is very crucial as they might still be owing current debts to be paid shortly. For example, A company might go for long-term loans if the market is in its favor. If all hands are on deck, they will make enough profits, which will outweigh their debts and keep them far ahead. Smart business owners prioritize keeping assets above liabilities.
Depleted assets translate to a reduced level of care, Woolhandler told NBC News, noting that equipment, buildings and technology are resources needed for patient care. “There are real dangers to the health care that people get if you deplete all the capital from a hospital,” she added. A liability is a debt or other obligation owed by one party to another party. Current liabilities are obligations due within 12 months or within an operating cycle. Check your financial health score to get a more detailed look at your spending and saving habits and find out how you can improve.

Liabilities in accounting: Why is managing them so important?
- It is usually payable to an external party (e.g. lenders, long-term loans).
- Companies must carefully monitor their payment obligations and ensure they have sufficient liquidity to meet these obligations on time.
- Although the current and quick ratios show how well a company converts its current assets to pay current liabilities, it’s critical to compare the ratios to companies within the same industry.
- They include bank account overdrafts, short-term loans, interest payable, and accounts payable.
- Portions of long-term liabilities can be listed as current liabilities on the balance sheet.
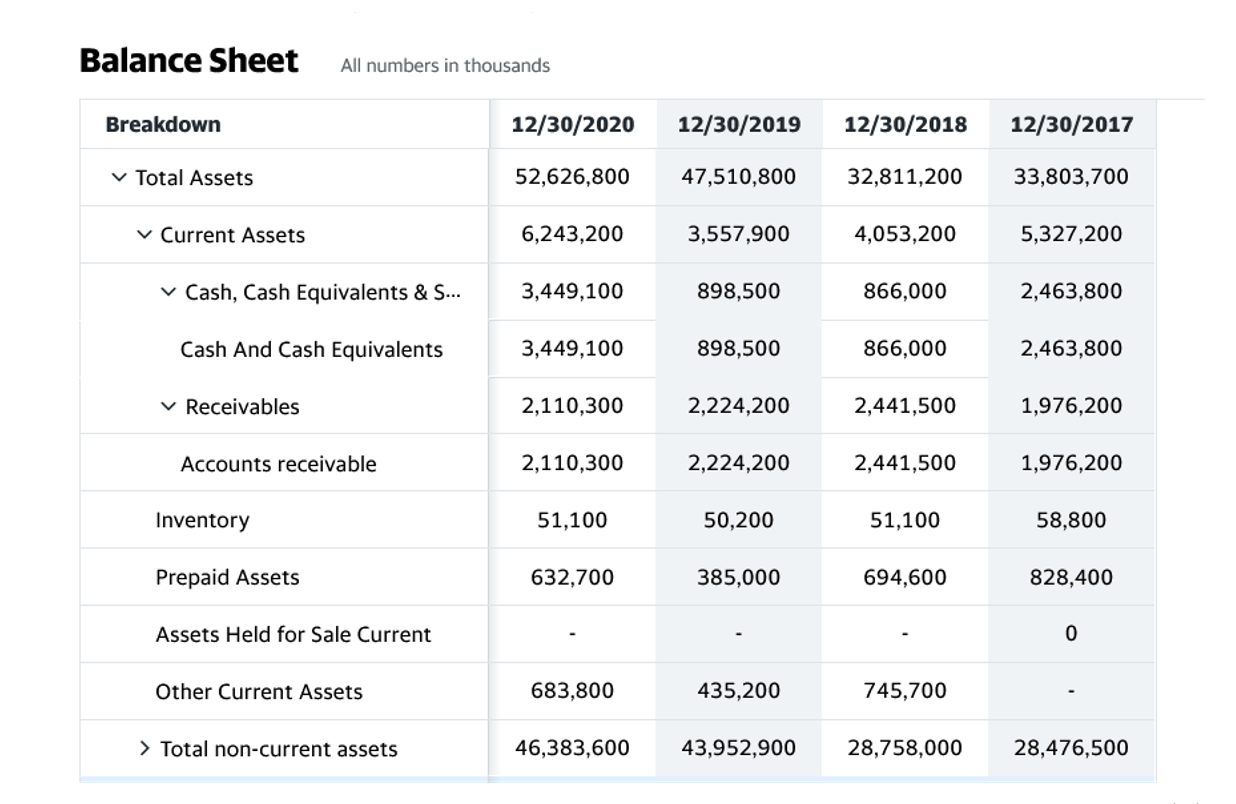
A liability is something that a person or company owes, usually a sum of money. Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. They’re recorded on the right side of the balance sheet and include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and what are the liabilities accrued expenses. Analysts and creditors often use the current ratio, which measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term financial debts or obligations. The ratio, which is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities, shows how well a company manages its balance sheet to pay off its short-term debts and payables.
The best way to track both assets and liabilities is by using accounting software, which will help categorize liabilities properly. However, even if you’re using a manual accounting system, you still need to record liabilities properly. Notes Payable – A note payable is a long-term contract to borrow money from a creditor. Bonds Payable – Many companies choose to issue bonds to the public in order to finance future growth. Bonds are essentially contracts to pay the bondholders the face amount plus interest on the maturity date.
What Is a Liability?
For example, banks want to know before extending credit whether a company is collecting—or getting paid—for its accounts receivable in a timely manner. On the other hand, on-time payment of the company’s payables is important as well. Both the current and quick ratios help with the analysis of a company’s financial solvency and management of its current liabilities. Total liabilities are the combined debts and obligations that an individual or company owes to outside parties. Everything the company owns is classified as an asset and all amounts the company owes for future obligations are recorded as liabilities. On the balance sheet, total assets minus total liabilities equals equity.
- Accounts payable is typically one of the largest current liability accounts on a company’s financial statements, and it represents unpaid supplier invoices.
- Current liabilities are used as a key component in several short-term liquidity measures.
- The primary classification of liabilities is according to their due date.
- Deferred tax liability refers to any taxes that need to be paid by your business, but are not due within the next 12 months.
- However, poor management of liabilities may result in significant negative consequences, such as a decline in financial performance or, in a worst-case scenario, bankruptcy.
- Liabilities consist of many items ranging from monthly lease payments, to utility bills, bonds issued to investors and corporate credit card debt.
- Any long-term liabilities should be able to be covered by revenue generated over time by assets.

